

So if my understanding is correct ( and please correct me if I am wrong, I do want to learn ), pinging loopback address tests the network card (physical layer), while pinging your own IP address or other IP addresses involves network layer. You can imagine localhost as the 'name' for the 127.0.0.1 address, much like how 'is the 'name' for Googles IP address. The following example shows valid IP address configurations on two loopback interfaces. There are 7 OSI layers: physical, datalink, network, transport, session, presentation and application layers.

Up to thirty-two IP addresses are supported on a loopback interface. You can configure multiple IP addresses on a loopback interface ( lo0 to lo7). In the same way, if you configure a loopback interface ( lo1) with IP address 172.16.101.8, you cannot configure another loopback interface ( lo2) with IP address 172.16.101.8. This means that the address cannot be used by a VLAN interface or another loopback interface.įor example, if you configure a VLAN with IP address 172.16.100.8/24, you cannot configure a loopback interface with IP address 172.16.100.8. The maximum number of IP addresses supported on a switch is 2048, which includes all IP addresses configured for both VLANs and loopback interfaces (except for the default loopback IP address 127.0.0.1).Įach IP address that you configure on a loopback interface must be unique in the switch. Most IP implementations support a loopback interface (lo0) to represent.
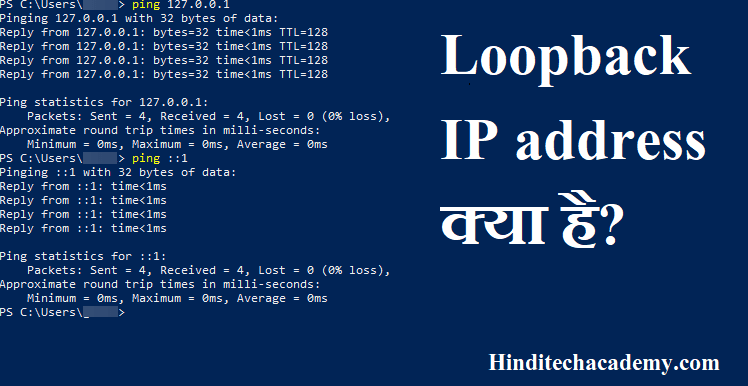
Loopback interfaces share the same IP address space with VLAN configurations. The Internet Protocol (IP) specifies a loopback network with the (IPv4) address 127.0.0.0/8. Instead, this network is used for loopback IP addresses, which allow for. 127.0.0.1 is the address most commonly used for testing purposes. However, the 127 network number isnt used by hosts as a logical IP address. Answer (1 of 5): It’s a pretty simple yet powerful tool in networking using a Loopback Address for routing updates, path selection and so on. Since the lower layers are short-circuited, sending to a loopback address allows the higher layers (IP and above) to be effectively tested without the chance of problems at the lower layers manifesting themselves. I tested how the router does summarization, what will be the cost of summarized routes, how you can do redistribution etc.You can configure a loopback interface only from the CLI you cannot configure a loopback interface from the WebAgent or Menu interface. 0.0.0.0 Explanation: Difficulty: Easy Section Reference: Categorizing IPv4 Addresses The range for Class A is 0127. Sometimes I used many loopback intefaces on the same router to test summarization of routes to other routers: I gave subnet numbers to them from a contiguous pool and summarized those subnets to advertise them to other routers. you can ping them, advertise them in routing protocols, etc. Loopback intefaces also can be used for testing purposes when you build a network, because they behave as normal interfaces, i.e.

In multicast, generally the loopback interface addresses are used to advertise the Rendez-vous Points for the same stability reason. Loopback addresses can be useful in various kinds of analysis like testing and debugging, or in allowing routers to communicate in specific ways. (Loopback intefaces do not go down unless the router goes down, in contrast with physical intefaces that may go down.) What is an IP loopback address A loopback address has been built into the IP domain system in order to allow for a device to send and receive its own data packets. It is primarily a means of testing the communications infrastructure. In BGP, you can use the loopback addresses to define the neighbor relationships to increase the stability of the neighbor relationship, if you have several physical paths to the same neighbor. Loopback (also written loop-back) is the routing of electronic signals or digital data streams back to their source without intentional processing or modification. In OSPF, the loopback inteface with the highest IP address will give the router id, if no router-id is specified under the routing process. On routers, loopback interfaces are used for several purposes, some examples follow:įirst, you should have an IP address assigned to the loopback interface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
